synopsis of recent work
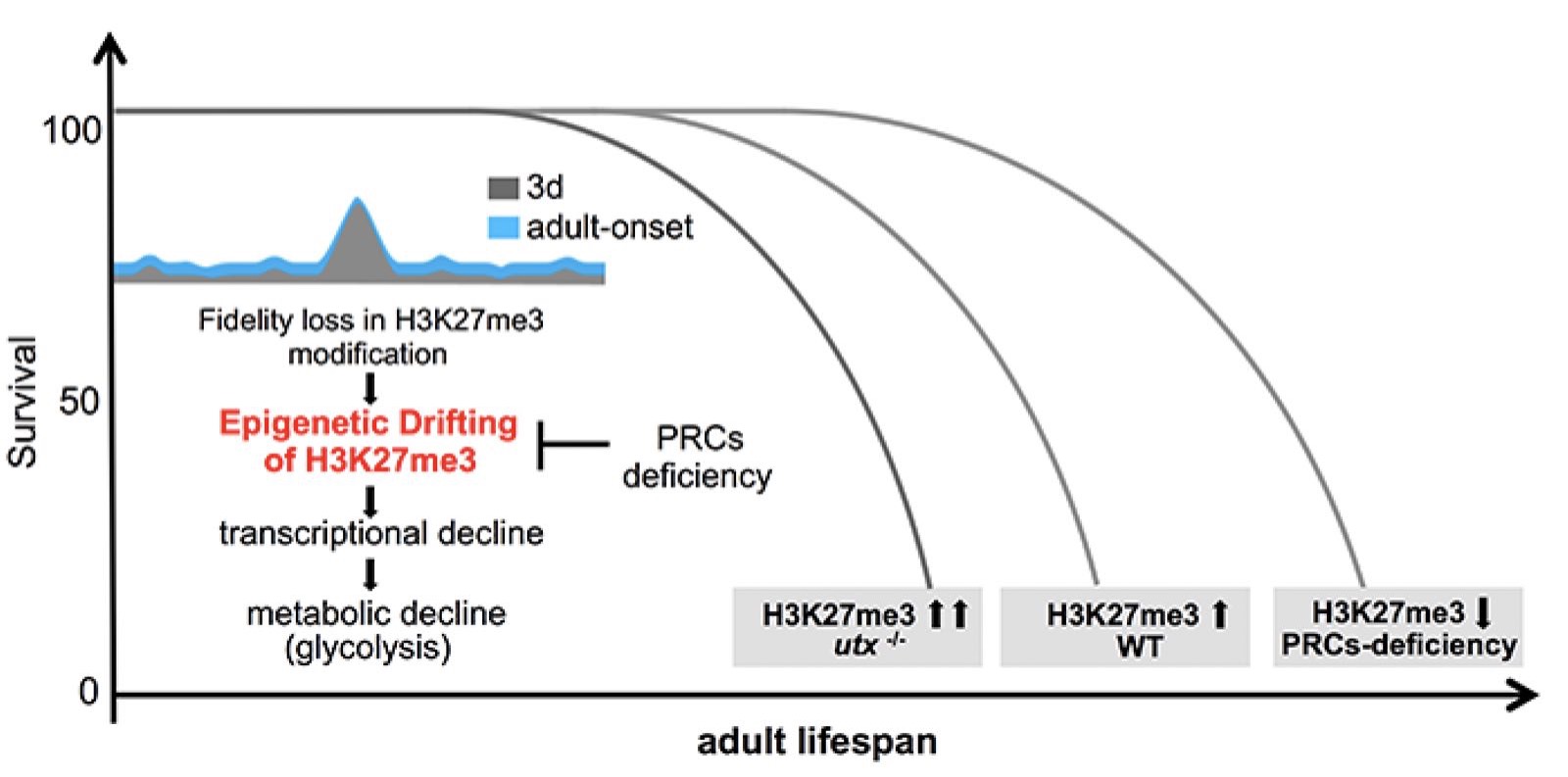
Epigenetic alteration has been implicated in aging. However, the mechanism by which epigenetic change impacts aging remains to be understood. H3K27me3, a highly conserved histone modification signifying transcriptional repression, is marked and maintained by Polycomb Repressive Complexes (PRCs). Here, we explore the mechanism by which age-modulated increase of H3K27me3 impacts adult lifespan. Using Drosophila, we reveal that aging leads to loss of fidelity in epigenetic marking and drift of H3K27me3 and consequential reduction in the expression of glycolytic genes with negative effects on energy production and redox state. We show that a reduction of H3K27me3 by PRCs-deficiency promotes glycolysis and healthy lifespan. While perturbing glycolysis diminishes the pro-lifespan benefits mediated by PRCs-deficiency, transgenic increase of glycolytic genes in wild-type animals extends longevity. Together, we propose that epigenetic drift of H3K27me3 is one of the molecular mechanisms that contribute to aging and that stimulation of glycolysis promotes metabolic health and longevity.
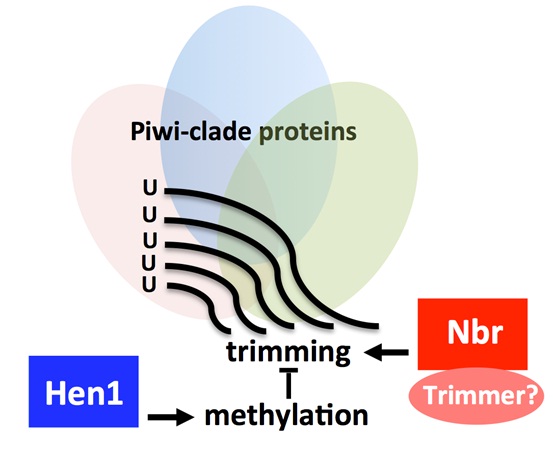
Antagonistic roles of Nibbler and Hen1 in modulating piRNA 3′ ends in Drosophila In eukaryotes, aberrant expression of transposable elements (TEs) is detrimental to the host genome. Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) of ∼23 to 30 nucleotides bound to PIWI clade Argonaute proteins silence transposons in a manner that is strictly dependent on their sequence complementarity. Hence, a key goal in understanding piRNA pathways is to determine mechanisms that modulate piRNA sequences. Here, we identify a protein-protein interaction between the 3′-to-5′ exoribonuclease Nibbler (Nbr) and Piwi that links Nbr activity with piRNA pathways. We show that there is a delicate balance in the interplay between Nbr and Hen1, a methyltransferase involved in 2′-O-methylation at the 3′ terminal nucleotides of piRNAs, thus connecting two genes with opposing activities in the biogenesis of piRNA 3′ ends. With age, piRNAs become shorter and fewer in number, which is coupled with the derepression of select TEs. We demonstrate that activities of Nbr and Hen1 inherently contribute to TE silencing and age-dependent profiles of piRNAs. We propose that antagonistic roles of Nbr and Hen1 define a mechanism to modulate piRNA 3′ ends.
Recent publications
2020
Hepatocyte-Specific TAK1 Deficiency Drives RIPK1 Kinase-dependent Inflammation to Promote Liver Fibrosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Shuixia Tan, Jing Zhao, Ziyu Sun, Shuangyi Cao, Kongyan Niu, Yedan Zhong, Han Wang, Linyu Shi, Heling Pan, Junhao Hu, Lihui Qian, Nan Liu*, and Junying Yuan*. Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences. 2020 doi/10.1073/pnas.2005353117
2019
Multidimensional Proteomics Identifies Declines in Protein Homeostasis and Mitochondria as Early Signals for Normal Aging and Age-associated Disease in Drosophila. Yang L, Cao Y, Zhao J, Fang Y, Liu N*, Zhang Y*. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2019 Oct;18(10):2078-2088. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA119.001621.
Ubiquitylome study identifies increased histone 2A ubiquitylation as an evolutionarily conserved aging biomarker. L Yang, Z Ma, H Wang, K Niu, Y Gao, L Sun, Y Geng, B Yang, F Gao, Z Chen, Z Wu, Q Li, Y Shen, X Zhang, H Jiang, Y Chen, R Liu, N Liu*, and Y Zhang*. Nature Communications 10, Article number: 2191 (Recommended by Faculty of 1000, https://f1000.com/prime/735813510)
Metabolic reaction network-based recursive metabolite annotation for untargeted metabolomics. X Shen, R Wang, X Xiong, Y Yin, Y Cai, Z Ma, N Liu, and Z Zhu. Nature Communications 10:1516 | https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09550
Age-dependent changes in transcription factor FOXO targeting in female Drosophila. A Birnbaum, X Wu, M Tatar, N Liu*, H Bai*. Frontiers in Genetics. 10, 312 2019
Multi-omic analyses reveal minimal impact of the CRISPR-Cas9 nuclease on cultured human cells. J Qiang, Z Ma, X Xie, L Shi, Y Geng, J Hu, R Liu, N Liu, and Y Zhang. Journal of Proteome Res. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00751
2018
Selenocysteine-specific mass spectrometry reveals tissue-distinct selenoproteomes and candidate selenoproteins. L Guo, W Yang, Q Huang, J Qiang, JR Hart, W Wang, J Hu, J Zhu, N Liu, and Zhang Y. Cell Chemical Biology 25 (11), 1380-1388. e4 2018
Epigenetic drift of H3K27me3 in aging links glycolysis to healthy longevity in Drosophila. Z Ma, H Wang, Y Cai, H Wang, K Niu, X Wu, H Ma, Y Yang, W Tong, F Liu, Z Liu, Y Zhang, R Liu, Z Zhu* and N Liu*. elife 7, e35368 7 2018 (Featured by Science Editors' Choice)
Quantitative ChIP-seq by adding Spike-in from another species. K Niu, R Liu, N Liu*. Bio-protocol DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2981.
Stable-isotope labeled metabolic analysis in Drosophila Melanogaster: from experimental setup to data analysis. Y Cai, N Liu*, ZJ Zhu*. Bio-protocol DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3015.
Necroptosis promotes cell-autonomous activation of proinflammatory cytokine gene expression. K Zhu, W Liang, Z Ma, D Xu, S Cao, X Lu, N Liu, B Shan, L Qian, J Yuan. Cell Death & Disease 9 (5) 11 2018
MiR-34 inhibits polycomb repressive complex 2 to modulate chaperone expression and promote healthy brain aging. J Kennerdell, N Liu, N Bonini. Nature Communications 9 2018
2017
Systematic analysis reveals tumor-enhancing and -suppressing microRNAs in Drosophila epithelial tumors. Z Shu, Y Huang, W Palmer, Y Tamori, G Xie, H Wang, N Liu and WM Deng. Oncotarget 1;8(65):108825-108839. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22226.
2016
Antagonistic roles of Nibbler and Hen1 in modulating piRNA 3′ ends in Drosophila. H Wang, Z Ma, K Niu, Y Xiao, X Wu, C Pan, Y Zhao, K Wang, Y Zhang*,and N Liu*. Development 143 (3), 530-539 30 2016
2015
Twin promotes the maintenance and differentiation of germline stem cell lineage through modulation of multiple pathways. Z Fu, C Geng, H Wang, Z Yang, C Weng, H Li, L Deng, L Liu, N Liu, J Ni, and T Xie. Cell reports 13 (7), 1366-1379,11
Prior to 2013
The microRNA miR-34 modulates ageing and neurodegeneration in Drosophila. N Liu, M Landreh, K Cao, M Abe, GJ Hendriks, JR Kennerdell, Y Zhu, and B Nancy. Nature 482 (7386), 519 312 2012
The Exoribonuclease Nibbler Controls 3′ End Processing of MicroRNAs in Drosophila. N Liu, M Abe, LR Sabin, GJ Hendriks, AS Naqvi, Z Yu, S Cherry, and B Nancy. Current Biology 21 (22), 1888-1893, 110, 2011
Hosting neurotoxicity in polyglutamine disease. N Liu, NM Bonini. Cell 127 (7), 1299-1300,8, 2006
A new role for microRNA pathways: modulation of degeneration induced by pathogenic human disease proteins. J Bilen, N Liu, NM Bonini. Cell Cycle 5 (24), 2835-2838, 79, 2006
MicroRNA pathways modulate polyglutamine-induced neurodegeneration. J Bilen, N Liu, BG Burnett, RN Pittman, NM Bonini. Molecular cell 24 (1), 157-163 254 2006
Identification of a nuclear localization signal in OCT4 and generation of a dominant negative mutant by its ablation. G Pan, B Qin, N Liu, HR Schöler, D Pei. Journal of Biological Chemistry 279 (35), 37013-37020, 79, 2004
Nuclear localization of the phosphatidylserine receptor protein via multiple nuclear localization signals. P Cui, B Qin, N Liu, G Pan, D Pei. Experimental Cell Research 293 (1), 154-163, 108, 2004
Identification of an 85-kb DNA fragment containing pms1, a locus for photoperiod-sensitive genic male sterility in rice. N Liu, Y Shan, F Wang, C Xu, K Peng, X Li, Q Zhang. Molecular Genetics and Genomics 266 (2), 271-275, 72, 2001
The distribution and copy number of copia-like retrotransposons in rice (Oryza sativa L.) and their implications in the organization and evolution of the rice genome. S Wang, N Liu, K Peng, Q Zhang. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 96 (12), 6824-6828 6, 1999
